|
|
|
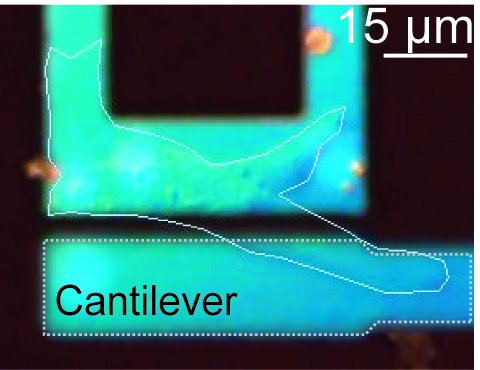
We report a 2-axis sensor designed to measure cellular force directly. The target cells were cultured on the sensor-pad (125 µm×15 µm) fabricated at the end of a piezo-resistive beam. The surface of the sensor was insulated and temperature compensation sensor was fabricated because the sensor was placed in culture medium (electrolyte-containing) and the temperature was maintained at 37 degC. The cells on the sensor was monitored concurrently by a microscope. The measured cellular force of a bovine arotic smooth muscle cell was 3.6~22 nN/µm2 and it was confirmed that the force resolution of the sensor (10nN) was sensitive enough for our purpose. The results shows that cellular force increase commensurately with the adhered area of the cell. This is the first report that measure cellular force directly by sensor.
References :
1.Uijin G. Jung, Hidetoshi Takahashi, Kiyoshi Matsumoto and Isao Shimoyama, “Cellular traction force measurement method using a MEMS force plate,”; SEB Annual Main Meeting 2014, A12.38, Manchester, UK, July 1-4, 2014.
2.Uijin G. Jung, Takuya Tsukagoshi, Hidetoshi Takahashi, Tetsuo Kan, Kiyoshi Matsumoto and Isao Shimoyama, “Traction force of smooth muscle cell during growth on a rigid substrate,” ; The 27th IEEE International Conference on Micro Electro Mechanical Systems (MEMS2014), pp. 290-293, San Francisco, USA, Jan. 26-30, 2014.[Proceeding]
|